Ozone for Pharmaceuticals - Process, CIP, Wastewater
Pharmaceuticals
Ozone is a sustainable and environmentally safe treatment for water that is chemical-free, energy-efficient and cost-effective.
For the pharmaceutical industry, Aclarus Ozone provides water treatment solutions for the following operational challenges:
Incoming water purity
Process water and Clean-in-Place (CIP) sanitation
Wastewater and re-use
Ozone Advantages for the Pharmaceutical Industry
Ozone is increasingly used in the pharmaceutical industry because it has numerous advantages over traditional disinfection methods. Supplementing or replacing an existing system with an ozone system has the potential to boost a company’s advantage over its competitors.
Ozone has the following advantages for pharmaceutical manufacturers:
✓ It is chemical-free and breaks down to oxygen after treatment
✓ Treats incoming source water to bottled-water standards
✓ Disinfects and sanitizes equipment and surfaces quickly, without chemicals
✓ Compliant with Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for surface sanitization.
✓ Neutralizes unhealthy minerals in the water, like iron, sulphur and manganese;
✓ Removes and colour, taste or odour
✓ Enables greater water conservation and re-use of wastewater
✓ Produced Onsite and On Demand, removing the need to purchase, store and physically handle chemicals.
Ozone for Pharmaceuticals, Proven Success
Provides The Highest Treatment Assurance
Proven To Reduce Costs, Time And Water Compared To Chemicals.
Unique Multi-Ability: Disinfection, Oxidation; Inactivation Of Many Chemicals.
Significant And Immediate Savings Vs Chemicals, Hot Water Sanitation.
Has Lower Life-Cycle Costs And Less Maintenance.
Aclarus Water Treatment Solutions
Incoming Water Purity
Incoming water purity has a direct impact on the quality of the final pharmaceutical product.
Ozone offers the fastest disinfection, even at low doses (e.g. <2ppm) for bacteria, viruses and cysts, as it ruptures cells upon contact. Unlike chemicals, ozone is not reliant on toxicity (slow absorption). Moreover, ozone does not allow bacteria or viruses to develop resistance or immunity to treatment.
Other technologies leave gaps in water treatment that can be filled by ozone:
Chlorine produces multiple types of chemical by-products and is a slow process for disinfection;
Reverse osmosis, while removing nearly all contaminants, does not provide sufficient disinfection, and bacteria can grow in stored water if untreated; and,
Ultra-violet light, common for sterilizing water, does not kill bacteria; rather, it only renders bacteria inactive and leaves them in product water. UV is needs specific conditions to operate effectively.
Ozone has no impact on pH levels in the water and leaves no residual, as it breaks down to oxygen before use. Ozone can be used “on demand” to solve multiple water treatment issues safely and efficiently. Regardless of the source of the water, ozone and post-filtration will quickly remove:
Pathogens:
Bacteria (E. coli, Streptococcus, Cholera, Pseudomonas, Mycobacterium)
Virus (Adenovirus, Legionella, Rotavirus, Salmonella, influenza, hepatitis, polio)
Cysts; (Giardia, Crypto, Cyclospora, E. Dispar)
Contaminants:
Metals - (Iron, Manganese, Sulphur, Lead, Arsenic)
Organics - (Biofilm, Algae, Tannin, Colour, NOM)
Inorganics - (Cyanides, COD)
Chemicals – (Chlorine, sulphur dioxide, and chlorine-containing organic by-products (e.g. trihalomethanes)
Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CECs):
Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products
Hormones, Antibiotics, Medications
Estrogen, Sulfamet, Oxycodone, Ibuprofen, Triclosan
Amphetamines, Cocaine, Opioids
PFAS (Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances - Teflon)
Micropollutants & Microplastics
Process Water and Clean-In-Place (CIP) Sanitation
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, the proper disinfection of equipment and surfaces throughout the production chain is critical to maintaining product quality and employee safety. Ozone meets the most stringent standards for sanitation at the lowest cost and environmental footprint.
Ozone is NF-61 certified and is compliant with Health Canada, the CFIA and the U.S. FDA for both product and surface sanitization. It is gentler than many common chemicals currently used for sanitation. It is safe for pharmaceutical products and adds oxygen to the water.
To preserve the quality of water throughout the entire production chain, ozone can be used in a Clean-in-Place (CIP) closed loop system that involves the cleaning and sanitizing all production equipment and surfaces – including machines, tables, floors, tanks, drain lines, and other areas.
Following industry standard practices, ozone is applied as a final rinse sanitation, using cold water only, to treat bacteria, viruses, fungi and more. No final rinse is needed as ozone breaks down in minutes to oxygen, leaving no residual to save time, water and power costs.
Wastewater and Re-Use
Ozone safely treats wastewater, helping to keep drain lines clear and only producing oxygenated water that is safe to discharge without concerns for septic systems and municipal requirements. It is a cost-effective treatment that enables pharmaceutical manufacturers to achieve regulatory compliance and reduce fees and fines.
Pharmaceutical wastewater will vary greatly depending on the application and medication being produced, with thousands of potential types. Knowing the specific chemicals and their levels in the wastewater helps determine the required ozone demand. Given the critical nature of the industry, wastewater from pharmaceutical production requires careful system design to ensure safety and efficiency.
Ozone Aclarus engineers assess the wastewater needs for each manufacturer and design a solution to fit the need through testing and/or pilot demonstrations. This is done to determine the level of treatment and ozone required (e.g. disinfection, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), etc.).
By using ozone in the CIP sanitation process, the run-off water requirements are lessened, “reducing at least by 50% the organic load in the cleaning waste waters produced” (Canut et al 2013). This is due to ozone’s ability to reduce COD and remove many contaminants prior to discharge.
Moreover, ozone-treated wastewater in a CIP closed-loop system can be re-used for non-potable purposes. This is an obvious environmental benefit at a time when freshwater shortages are occurring, and also results in cost savings for pharmaceutical manufacturers.
While effective on its own, ozone can be combined with other oxidation treatments to form Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP). AOP can offer even more enhanced treatment by forming hydroxyl radicals, amplifying the treatment effect. The most typical form of AOP is achieved with a combination of ozone and UV or ozone and peroxide.
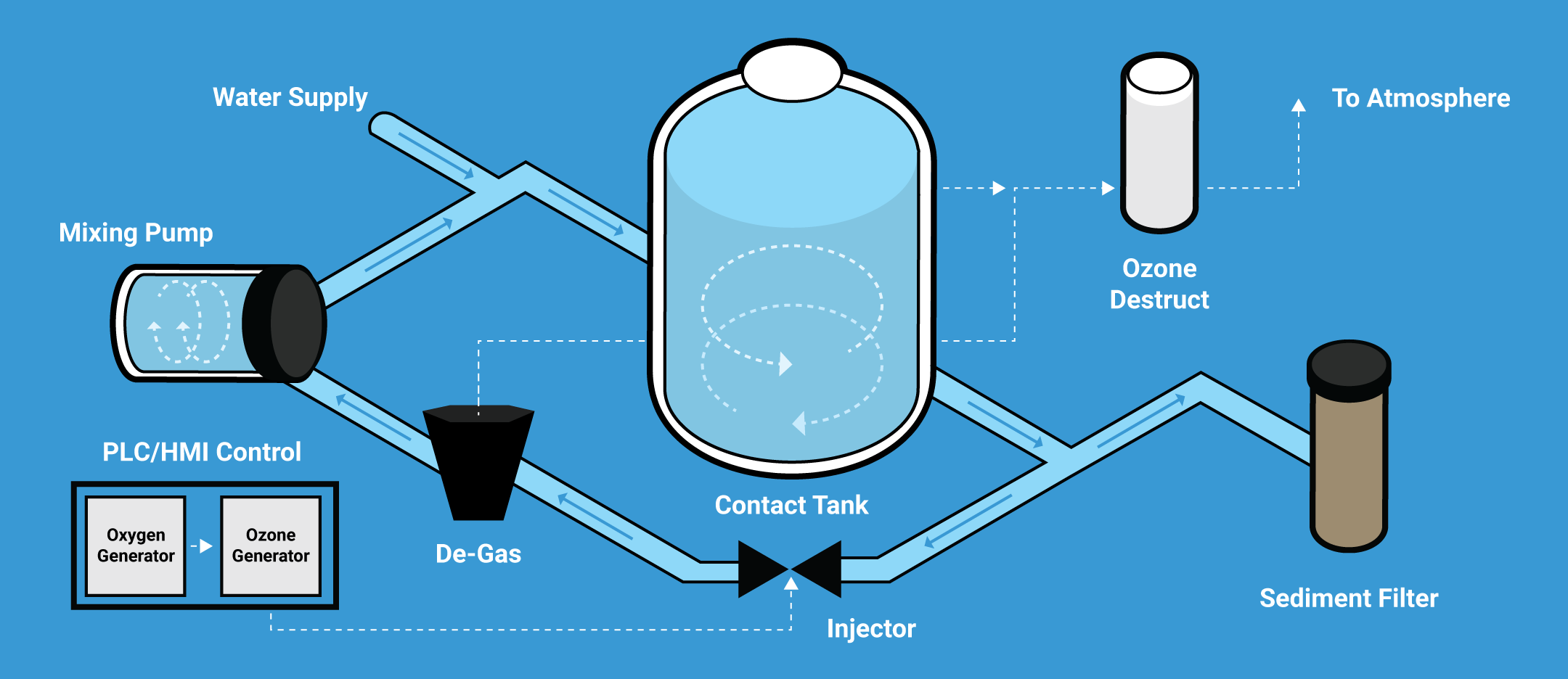
Aclarus Ozone Systems Overview
Aclarus Ozone systems generate ozone on-site, with an ozone level calibrated for each application and flow rate. The systems are scalable to accommodate microbreweries to large-scale operations and they offer advanced ozone generation, mixing and control systems for reliable and accurate treatment.
Aclarus systems are easily retrofitted into existing facilities and are modular, to allow expansion when required. They can range from simple on/off systems to fully programmable control systems with remote monitoring, alarm integration, ozone dose control and more.
Aclarus’ advanced saturation systems maximize ozone transfer into water at an average of over 90% compared with traditional transfer rates of approximately 10%. Using inline monitors, the water is measured for automated control to either increase or decrease the ozone level to remain at a setpoint for optimal function.
Following ozonation, the water is filtered and then ozone is either removed for incoming use or remains in the water for use in sanitation. In many cases ozone can work in a closed loop CIP to greatly lessen water use and waste.
Aclarus Ozone systems also remove excess ozone from the water and destroy it, limiting potential off-gassing by using integrated air monitors for safe workspaces.
Cost Comparison
There is a common perception that ozone is an unaffordable approach to water treatment. In fact, the average operational cost of the Aclarus Ozone System is approximately 5-10 cents per 1,000 litres of treated water, offering the lowest Lifetime Operating Cost (LOC) compared to other technology and a quick Return on Investment.
Aclarus Ozone systems are found in a wide range of applications, including industrial and municipal operations, precisely because they are a cost-effective and reliable treatment. Aclarus advanced and affordable designs have brought ozone to multiple markets that have not previously used ozone.
References
Almomani, F. A., Shawaqfah M., Bhosale, R. R., Kumar, A., 2016. Removal Of Emerging Pharmaceuticals From Wastewater By Ozone-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes. Environmental progress and sustainable energy, American Institute of Chemical Engineers, Environ Prog.
Canut, A., Llorca, I., Soro, R, Pascual, A 2013. Reducing costs by integrating ozonated water in the CIP systems Research Association for Food Industry (ainia). Quality, food safety and environment department Valencia.
Djap, M. A., Yargeau, V., 2015. Removal Of Contaminants Of Emerging Concern (CECS) From Wastewater Using Pilot Ozonation Technology. Thesis paper, Department of Chemical Engineering McGill University, Montreal
Hanley-Onken, Erika 2013. Ozone: A New Water Management Paradigm. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Magazine.
Szabová, P., Hencelová, K., Sameliaková, Z. et al. 2020 Ozonation: effective way for removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewater. Monatsh Chem 151, 685–691 (2020).
Do you have an ozone related question?
Read past responses or submit your question for Adam Doran Aclarus Co-Founder!